- The Meaning of Critical Thinking: A Key Skill for Navigating Today’s Information Landscape - November 3, 2025
- Grandparents Can Develop Activist Grandchildren - September 29, 2025
- Top Six Reasons Credit Union Benefits Are a Smart Choice Over Banks - August 18, 2025
Last Updated on February 27, 2025
In this post, I cover the importance of activists for animal rights and how animal welfare laws are a critical tool in the fight. Sadly, animals are often considered belongings rather than beings. And they cannot speak out to access the rights and protection they deserve. Animal rights are critical to improving animal welfare, preventing animal cruelty, promoting responsible pet ownership, and encouraging wildlife conservation.
By implementing animal welfare laws, activists for animal rights can better protect and promote the rights and well-being of animals.
Animal Activism Takes Many Forms
If you want to become an animal rights activist, you have my eternal gratitude! In my 5-Step Activism Path, I help new activists find the right activism opportunity based on their passion, skills, and motivation. If you are unsure how to focus your passion for animal activism, consider trying the 5-Step Path. You’ll be more motivated and impactful with an approach tailored to you.
Although I primarily discuss animal welfare laws in this post, you can make a difference for animals in many ways. Browse the areas of animal activism below.
Animal Welfare Laws
Activists for animal rights can implement animal welfare laws that range from preventing animal cruelty and exploitation to wildlife conservation. Examples include bans on specific practices like factory farming and legal protections for wildlife.
Corporate Campaigns
Corporate campaigns press companies to adopt humane practices like cage-free eggs or plant-based menu options. For example, the Humane League successfully pressured major food brands to commit to cage-free eggs.
Advocacy
Advocacy is making people aware of animal rights issues. You can use media and public events to expose animal cruelty and inspire empathy, such as street outreach and Meatless Mondays initiatives. The World Wildlife Fund shares wildlife success stories and conservation tips on social media.
Direct Action
Direct action includes protests, demonstrations, and nonviolent resistance to highlight unjust practices. Examples include activists chaining themselves to factory farms to stop operations and Sea Shepherd’s campaigns against illegal whaling and fishing in international waters.
Animal Rescue and Sanctuaries
Animal rescues and sanctuaries provide homes and care for abused or neglected animals and educate the public about animal welfare. Farm Sanctuary and similar organizations highlight the plight of farmed animals, and wildlife rehabilitation centers advocate for habitat protection.
Scientific and Technological Solutions
Science and technology can make a difference for animals. Examples include innovation in plant-based and cultured meat technologies, alternatives to animal testing, and satellite tracking to monitor and protect endangered species.
Social Media Campaigns
Social media campaigns are a form of advocacy using platforms like Instagram and YouTube. Petitions and challenges can go viral using the power of social media.
Research
Research and statistics can support campaigns and make compelling cases for change. Examples include citing studies on the environmental impact of factory farming and survey results showing consumer demand for cruelty-free products.
Choose What Matches Your Skills and Motivation
Being a part of the animal rights movement is wonderful. But it is easy to get overwhelmed with all the areas that need attention, and it is crucial that you choose the right place for you, one that uses your unique skills and motivation. Focusing allows you to develop expertise and stay motivated to avoid burnout. Then, trust that others are doing the same in their areas of animal activism.
The Importance of Animal Welfare Laws

In the rest of this post, I cover the significance of these laws and explore how you can use legislation to advocate for animal rights.
Animal welfare laws encompass diverse issues and are vital in preventing cruelty and abuse. They set standards for treating animals in various settings, including pets, farm animals, and wildlife. Laws allow authorities to intervene in cases of neglect or abuse, ensuring that animals are treated with respect. This holds individuals accountable for their actions and promotes a culture of responsibility towards animals.
Minister and activist Roland Halpern volunteers for Colorado Voters for Animals. This organization advances animal welfare laws in their state. Recently, I was privileged to participate in a webinar featuring his work, which you can also access and view.
Colorado Voters for Animals has successfully banned wild animal performances in circuses, increased animal cruelty penalties, and allowed citizens to enter locked vehicles to rescue dogs or cats in distress.
In the webinar, Halpern emphasizes the importance of legislation as an animal welfare method. He prefers legislation over protests, lobbying, and negotiating with companies. Although each method provides a degree of awareness of the cause, only legislation enforces the desired behavior.
“I like to point out that promises are not laws, and we get involved a lot of times where a company promises they’re going to do something or not do something, and that’s just a promise. It’s not a law, so it’s typically not enforceable, even if it is a contract.” ~ Roland Halpern
Halpern’s work is focused on state legislation rather than federal work. There are typically fewer legislators that have to be won over at the state level. Your mileage may vary depending on your state because of the differences in state legislatures.
In his presentation, Halpern provides a nice overview of how to start the process, how a bill becomes a law, and some of the pitfalls you might encounter.
History and Evolution of Animal Welfare Laws
Animal welfare laws have a long history, stretching back centuries to when ancient cultures like Egypt and Greece honored animals through religious beliefs and customs. But it wasn’t until the 19th century that formal legal protections really took shape. In 1824, the founding of the Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals in the United Kingdom marked a turning point. This organization combatted cruelty and paved the way for future animal welfare laws.
A significant milestone came in the United States with the Animal Welfare Act of 1966. This legislation set the first federal standards for the humane treatment of animals in research, transport, and exhibition. Over the years, updates to the law have strengthened protections, reflecting an evolving understanding of animal welfare.
Hat tip to Tobias Leenaert of the Vegan Strategist for educating me about an interesting method of legislation. The Animal Labour Union organizes for working animals and attempts to gain rights that human workers enjoy. Working animals include farm animals but also bees, police dogs and horses. Their work is based on the rights certain working animals receive that mimic human labor law.
“… in some countries, certain animals have already gained limited rights derived from labor law—combat and police animals receive pension rights, while zoo animals are granted rest periods. When we begin discussing animals in terms of labor (similar to how we’ve reframed the work of prisoners or women’s invisible household labor), this can transform perceptions and values.” ~ Animal Labour Union
The approach to animal welfare continues to shift as we learn more about animals’ psychological needs. Laws now go beyond simply preventing cruelty to promoting well-being. But there is still a long way to go.
The Impact of Animal Welfare Laws on Animal Rights Activism
Animal welfare laws have shaped the animal rights movement. Setting clear legal standards for how animals should be treated gives activists a solid foundation for their work to hold individuals and industries accountable for cruelty and push for more humane treatment. The law creates enforceable mandates, making animal welfare a responsibility that cannot be ignored.
Beyond legal enforcement, animal welfare laws also highlight the realities animals face. Activists often run educational campaigns that expose issues in industries like factory farming and entertainment. This helps people connect the dots between their choices and the well-being of animals, driving support for even stronger protections.
Key Provisions and Regulations in Animal Welfare Laws
Animal welfare laws cover a wide range of protections designed to ensure animals are treated with care. A significant focus is preventing cruelty and neglect by making it illegal to harm, abandon, or deny animals food, water, shelter, and medical care.
Another critical area these laws address is the treatment of animals in experimentation. Many countries have strict guidelines to ensure that animals used in scientific studies are treated humanely. This means minimizing pain and distress and exploring alternatives before involving animals in research. These measures reflect a growing awareness that scientific progress shouldn’t come at the cost of ethical treatment.
Animal welfare laws also focus on responsible breeding and pet ownership. Regulations often require ethical breeding practices, oversight of pet stores, and programs to encourage spaying and neutering to help control overpopulation. These efforts reduce the number of stray animals and ensure that pets are bred and sold in humane conditions.
Success Stories: How Animal Welfare Laws Have Made a Difference

Farm animal welfare has also seen major strides thanks to legislative efforts. Laws that improve conditions for animals raised for food have addressed issues like confinement, transport, and slaughter practices. A standout example is California’s Proposition 2, which granted farm animals more space to move and express natural behaviors. This victory improved the lives of millions of animals and sparked a nationwide discussion about ethical farming practices.
Wildlife conservation is another area where animal welfare laws have made a powerful impact. Stronger regulations against poaching and illegal trafficking have helped protect endangered species, leading to significant population recoveries and habitat preservation. These successes show that progress can be made in safeguarding wildlife with proper legal protections.
The Humane Society reports successes in several states. Massachusetts enacted a law prohibiting the use of elephants, big cats, primates, giraffes, and bears in traveling shows. Legislation in Pennsylvania protects the pets of survivors of domestic violence, helping them to escape abusive situations without having to leave their companion animals behind. A law taking effect in Oregon punishes people who create and distribute of videos, photos, or other visual recordings of animal abuse.
Outside of the United States, the power of advocacy shows as well. The European Union is establishing uniform standards across member countries, which is a way to ensure those oppressing animals don’t move operations to another country. The standards cover dog and cat breeding, housing, handling, and reproduction. In the United Kingdom, ministers focus on the smuggling and treatment of puppies and kittens.
Greyhound racing has a history of mistreatment of animals, and many places have outlawed this type of gambling. New Zealand will ban the sport and implement a process to provide homes for the dogs.

Challenges and Controversies Surrounding Animal Welfare Laws
Even with the progress made in animal welfare laws, challenges continue.
Influencing Legislators
In his webinar, activist Halpern highlights many challenges in implementing animal welfare laws. One challenge he mentioned was enlightening, and that was the ways that legislators consider feedback from citizens. In this screenshot, Halpern shows the influence levels of various advocacy types. In-person visits are most influential, while form email messages are less so.
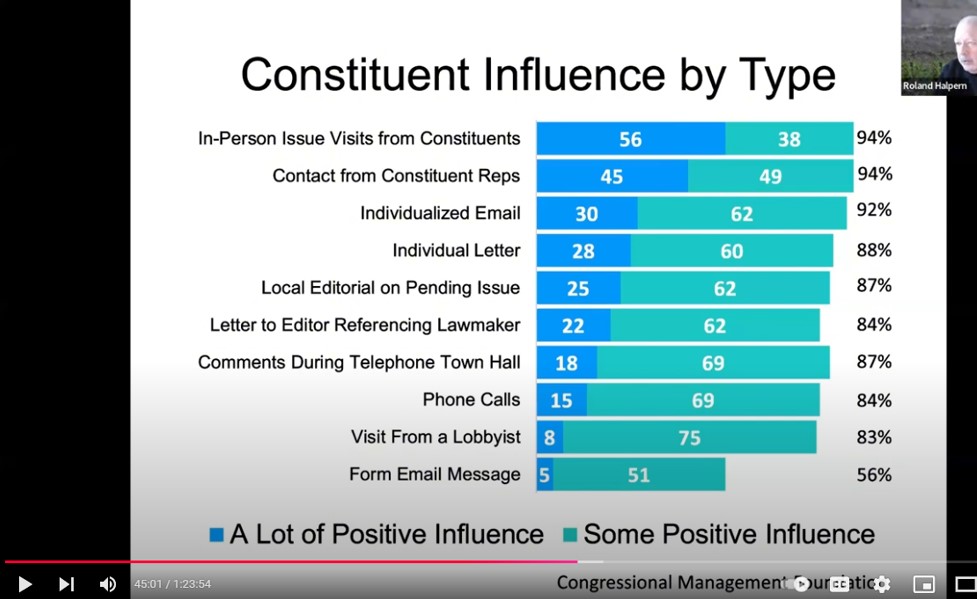
Uneven Protection and Enforcement
One of the biggest issues is the uneven coverage across different regions. Some areas have strong regulations and strict enforcement, while others have weak protections.
“A couple of years ago we tried to pass legislation on a statewide basis that would ban pet stores from selling dogs or cats that came from commercial breeders. Those laws did not pass. We got defeated by agriculture that said it’s dogs and cats this year, but if this bill passes, you’re going to be coming after pigs and chickens next year,” and so there was enough support from the agricultural community to defeat it.
So, we changed the game…and what we’re doing now is we’re going to city councils in towns where they don’t have pet stores that sell dogs and cats, and we’re getting ordinances passed that prohibit any future sale of dogs or cats in those particular towns and cities, and we’ve so far been able to pass it in thirteen. We’re working on the city of Denver next, and the idea is we’re working towards a critical mass, and once we get enough cities and towns to say we’re not going to allow this, we’re going to go back to the state and say, “Look, 50% of the towns and cities in Colorado are saying no, it’s time to pass a law on a statewide basis.””
Uneven protection and enforcement leaves gaps in animal protection, allowing organizations to take advantage. We must push for more consistent legal protections.
Animal vs. Human Interest
Another challenge is the tension between animal welfare and human interests, such as economic growth and scientific progress. Industries push back on animal welfare laws because they prioritize profits over animal well-being. That means we must carefully navigate the political landscape, educating lawmakers and the public on the importance of humane treatment without dismissing people’s concerns about jobs and scientific innovation.
Cultural Differences
Another challenge is cultural differences and how they shape animal welfare. What one community sees as inhumane may be considered normal in another. These differing viewpoints make it challenging to create universal animal welfare standards.
Carnism, coined by psychologist Melanie Joy, describes the invisible belief system that conditions people to see certain animals as food while others are cherished as companions. This deeply ingrained ideology shapes our cultural norms and perceptions, making it easier to disconnect from the realities of animal agriculture. The agriculture lobby, driven by profit, works hard to reinforce this disconnect, ensuring that people continue to consume animal products without questioning the ethical implications. If more people recognized the connection between the animals they love and those on their plates, public attitudes could shift. This awareness could drive stronger animal welfare laws, challenging the status quo and pushing for policies prioritizing compassion over consumption.

Halpern describes the care they take in their advocacy work to change the language that describes animals and animal rights.
“… we’re trying to move them more to being recognized as sentient beings and being something more than a toaster. We’re toying with using guardian rather than owner… we’re hoping that over time we can make that become the common language…”

As the screenshot shows, gradually changing how we describe animals and their relationship to humans can help change overall perspectives. Rather than ‘harvesting’ animals, companies are ‘killing’ or ‘slaughtering’ them. Using the words ‘cow’ and ‘pig’ instead of ‘beef’ and ‘pork.’ He also mentions that people tend to react more positively to the term ‘plant-based’ than ‘vegan.’
Conclusion: The Role of Activists for Animal Rights in Animal Welfare Laws
Activists for animal rights are critical for stronger animal welfare laws. I hope you will consider making a difference for animals if this is the cause closest to your heart.
READ NEXT







